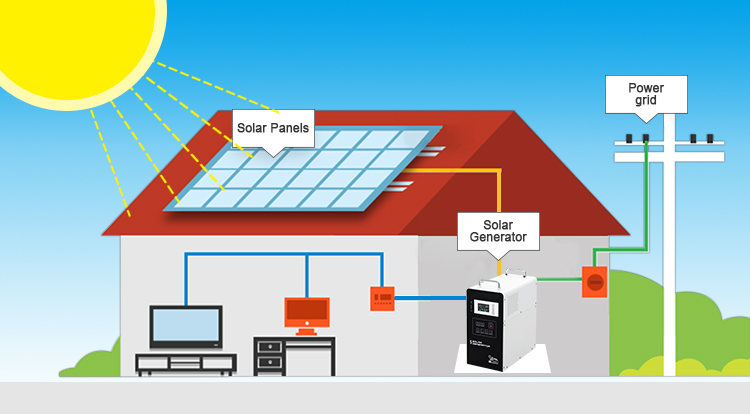
Solar energy is becoming more prevalent every day, but who discovered solar energy? Albert Einstein was considered as the father of solar cells. The history of solar power began in 1954, with just a few small steps, driven by scientists and inventors.
It was initially a promising but pricey replacement for fossil fuels. The industry has developed, and it is now a practical and affordable technology that is swiftly displacing coal, oil, and natural gas in the current energy market.
The most significant historical figures and occasions that influenced the advancement of solar technology are highlighted in this timeline. Keep reading and learn more about solar energy.
Table of Contents
History of Solar Energy
You could make the pedantic claim that very old bacteria were the ones who first discovered solar energy. Since the first microbes acquired the ability to engage in photosynthesis roughly 2.3 billion years ago, the sun has been the primary energy source for all life on Earth.
The Great Oxygenation Event, which was brought on by the release of oxygen gas as a byproduct of photosynthesis, was a devastating environmental catastrophe that ironically resulted from this. While these first solar powered organisms caused a mass extinction, solar power today might hold the key to preventing a planetary crisis.
Read More: Is Solar Energy Kinetic Or Potential?
Where Did Modern Solar Power Get Started?
Modern solar power has its origins in 1839, according to historical records.
A.E., a young French physicist, arrived at this time at the age of 19. The photovoltaic effect was discovered by Becquerel, whose area of interest had previously been phosphorescence and luminescence. He discovered that electrical current was produced when gold or platinum plates were immersed in a solution and then exposed to uneven solar radiation. Scientists from all over the world seized upon this discovery.

French mathematician August Mouchet started filing patent applications for solar-powered engines in the early 1860s. The first solar-powered printing press was created by Mouchet and his assistant Abel Pifre, who also displayed their solar-powered engine at the Universal Exhibition in Paris in 1878 and were awarded a gold medal for their efforts.
Unfortunately, Mouchet’s work was innovative at the time. His funding was cut off after the French government decided that solar power was not commercially viable. Thankfully, advances in solar technology continued.
How Did Solar Power Get Commercialized?
The first functional selenium solar cell was developed by American inventor Charles Fritz in 1883.
The first actual solar cell was created and patented in 1888 by a Russian scientist by the name of Aleksandr Stoletov. The initial industrial solar water heater was patented in 1891 by Baltimore inventor Clarence Kemp. Famous physicist Albert Einstein’s paper on the photoelectric effect and how light packets carry energy was published in 1905, which catapulted solar power into the public eye.
Following Einstein’s historic findings about the underlying mechanisms of the photoelectric effect, more advancements would follow. The first contemporary solar cell was created by Bell Labs in 1954 thanks to this new knowledge. This project was extremely inefficient even though it helped to develop solar energy technology as we know it today. Compared to the $2–$3 per watt charged by coal-fired power plants at the time, it cost $250 to produce just 1 watt of electricity.
Solar power was used in 1958 by the Vanguard 1 spacecraft as a backup energy source because solar cells at that time were still suitable for use in space. A solar cell with 10% efficiency was created a year later, but it was primarily used in spaceflight.
Related Post: How Does Solar Energy Affect the Environment?
The Future of Solar: New Improvements in Photovoltaic Cells
The design of highly efficient, lightweight, and flexible solar cells has become a focus of research in recent years. The spectrum of light that a solar cell can convert into energy has been expanded, strengthened, and protected by manufacturers.
This indicates that only 15% of the light they receive is converted into usable electricity. Solar panels are becoming more efficient thanks to ongoing scientific research into new technologies that can increase efficiency.
Advances in solar energy storage technology are also being developed, and new developments like light-sensitive nanoparticles and gallium arsenide may be able to capture sunlight more effectively than current PV cells. Just recently,
New solar cells created from cutting-edge materials will keep improving at converting light into electricity as solar technology advances. Combined with increasingly lower cost, solar power is poised to be one of the most important renewable energy technologies of the coming decades.
Read More: Is Solar Energy Renewable or Non-Renewable?
FAQs
Who Made Solar Panels?
Take a light step back to 1883 when New York inventor Charles Fritts created the first solar cell by coating selenium with a thin layer of gold.
When Were Solar Panels First Used on Houses?
The University of Delaware constructed the first ever solar building and called it Solar One in 1973.
Who Invented Solar Light?
American inventor Charles Fritts, perhaps the man best described as ‘the inventor of solar lights.