The purpose of this article is to explain how does solar energy work step by step and what advantages using solar energy can have for the environment.
While most people are aware that solar panels convert sunlight into usable electricity, not everyone is familiar with the science involved. Thus, if you’ve ever wondered, “How does solar energy work”, we’ve created this guide that explains the process in great detail.
Let’s examine solar power’s operation simply and sequentially.
Table of Contents
What is Solar Energy?
Every home on the planet, not just those in the United States, can get their electricity from solar energy, which is the solar radiation that the Sun emits. The Earth receives enough of this renewable energy every day. What a potent renewable energy source that is!
The most popular method of utilizing solar energy that humans have developed is the use of photovoltaic (PV) solar panels, which transform the sun’s energy into usable electricity.
Solar energy can and should play a significant role in the transition away from fossil fuels and conventional power plants, according to Palmetto, a pioneer in the clean energy transition.
Read More: Is Solar Energy Kinetic or Potential?
How Does Solar Energy Work?
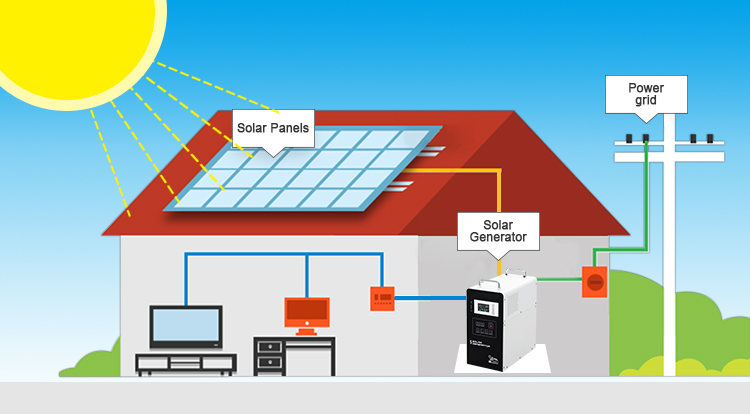
Step 1: Solar Panels Convert Sunlight to Energy
During the day, sunlight strikes solar panels, which they then use the photovoltaic effect to convert into energy. To put it simply, solar panels are made of silicon cells, which act as the active component and produce free electrons that travel through an electrical circuit when exposed to sunlight. Here is a detailed explanation of how solar panels operate.

The quantity of solar panels you will need for you install depends on a number of factors:
- The amount of sunshine you receive in your location
- The angle and orientation of your roof
- How much energy you typically consume in winter and summer
Step 2: Solar Inverter Converts from DC to AC Electricity
The solar inverter, which is typically installed somewhere close to the switchboard, is connected to the direct current (DC) electricity generated by the panels via electrical cable. The task of the solar inverter is to convert the direct current (DC) energy to alternating current (AC), which is used by regular appliances in a home or business. The size of the solar panel array must be taken into consideration when designing the various types and brands of inverters.
Step 3: Switchboard Routes Solar Energy to Home Appliances
After being converted to AC, the electricity is connected to the switchboard so that it can be used as a power source. The use of cheap solar energy will be prioritized if the house is also connected to the grid; however, if more energy is needed, it can be seamlessly obtained from the grid. The excess energy generated by the solar system may be “exported” back to the grid for use elsewhere on the network if it is producing more energy than is required.
A “battery-compatible” hybrid inverter or the switchboard can be used to connect solar batteries; for more information on batteries, see the section below.
Step 4: Utility Meter Records
Once solar has been installed, the responsible retailer must switch the current meter out for a bi-direction meter. The meter can then track all the energy used in the home as well as the amount of solar energy exported back to the grid. The household frequently has to pay a small fee to switch over to a new meter. The recorded electricity that is exported back to the grid can earn a “feed-in tariff”
Step 5: Grid Rules Define System Permissions
The business in charge of maintaining and owning the grid (poles and wires) in your neighborhood is known as a Distributed Network Service Provider (DNSP). Although for residential customers this is hidden and is included in your electricity retailer bills, a portion of your energy costs are paid to the DNSP as a contribution to the network’s maintenance and operational costs. The amount of solar that can be installed and whether you are allowed to export energy back to the grid vary slightly between each DNSP. Here is our guide where you can find a breakdown of the laws in each state.
As a general guide:
- Most DNSPs permit solar up to 5kW (inverter-size) with permission to export via a relatively automated approval process
- For commercial projects over 30kW a network protection device is required
- For commercial projects over 100kW a more detailed approval process usually is required meaning an engineering study will need to be completed to approve the system – and there might be some design alterations required for the install to be approved
You May Also Like: What Makes Solar Energy Green Apex?
Types of Solar Panels
There are 3 types of solar panels: polycrystalline, monocrystalline, and amorphous silicon.
Monocrystalline
A single, sizable silicon block constitutes a monocrystalline solar panel.
The efficiency of these silicon cells surpasses that of polycrystalline or amorphous silicon. Due to their labor-intensive manufacturing process, monocrystalline solar panels are typically more expensive than their polycrystalline counterparts.
Monocrystalline cells have a characteristic black appearance, making them easily identifiable.
Polycrystalline
Polycrystalline solar cells are also silicon cells. They are the result of melting several silicon cells together, as opposed to being shaped into a big block. The silicon molecules are melted and then fused into the panel itself.
Although less expensive than mono cells, polycrystalline solar panels are less efficient than those.
Poly solar panels are distinguishable by their typical bluish color.
Amorphous Silicon
Amorphous Silicon cells are used to create the newer flexible solar panels.
These cells lack crystalline structure. They are instead fastened to glass, plastic, or metal objects. They are typically extremely skinny, making them lean and pliable.
These solar panels are less efficient than monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels, despite the fact that they can be quite useful.
What Are the Benefits of Using Solar Energy?
Renewable Energy Source
Like many other energy sources, solar energy is a trustworthy, clean, renewable energy source that we can harness anywhere on earth, on a near daily basis
For as long as there is a sun, solar energy will be available. According to scientists, this should be the case for at least another 7 to 8 billion years.
Lowers Electricity Bills
Your utility bills will go down each month as a result of using less energy from the grid thanks to solar panels. What is the reduction in size? Well, this depends on your solar system
Many Applications
Solar energy can be applied in photovoltaic systems to generate electricity. But you can also use it to generate heat (solar thermal).
In areas where access to clean water is scarce, solar thermal can distill water.
Think solar bricks when picturing how solar energy will likely be incorporated into building materials in the future.
Affordable Maintenance Costs
You can expect solar panels from a reputable manufacturer, like SunPower, to last between 25 and 30 years after installation.
To ensure you maximize your panel’s solar absorption rate, maintenance includes a quick cleaning twice a year.
The only component that requires replacement is the inverter, which you can do every five to ten years because there are no moving parts, so there is typically little wear and tear. This indicates that, after making your initial investment in solar energy, you can anticipate paying relatively little in ongoing maintenance expenses.
Tech Development
Nanotechnology and quantum physics will undoubtedly advance in the future.
The efficiency of solar panels would be greatly increased, and the electrical output of solar systems would double or even triple as a result!
Also Read: Is Solar Energy An Ecosystem Service?
Key Takeaways: How Does Solar Energy Work?
When it comes to answering the question, “How does solar work?” we believe the benefits of solar energy for your home are undeniable. You can increase your independence from the electricity grid, decrease your reliance on the grid, lower your utility bills, reduce your carbon footprint, and do a lot more.
Understanding solar energy is useful for utilizing those benefits. Going solar at home is simpler than you might think, especially when you have a dependable partner like Palmetto by your side. From the sun hitting your solar panels to extra generation getting stored in your batteries.
Read More: What Do Plants Use Solar Energy For?